I ended up thinking about Debord’s Society of the Spectacle (1967) whenever I opened up Twitter this past week.
I mostly blame the clown-car/lynch mob that was Trump’s Republican National Convention (America, you have my bewildered sympathies). The ghastly God-I-wish-this-were-surreal-but-nope-it’s-reality sense of overwhelm that the convention engendered in me, even from the comfort of my securely-Canadian couch, was ugly. Add in the recurring black death and hashtag resistance that populates my Twitter feed all too often, the increasing regularity of mass-scale terrorism and retaliation, even the banning of professional troll @Nero from Twitter for unleashing all sorts of racist, misogynist hell against Ghostbusters’ Leslie Jones…it all adds up, for me, to a societal social contract that my existing conceptual tools are inadequately equipped to deal with.
Because what the hell is all this hot mess if not Spectacle with a capital S? (plus some other words that start with S and end with “storm”)…
#MakeAmericaGreatAgain#TrumpPence16 pic.twitter.com/gCzHX1nyxD
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) July 24, 2016
So. Debord’s been niggling at the back of my mind. He defines the spectacle as “a social relationship between people that is mediated by images” (p. 5).
(Caveat: I am a very casual reader of Debord. I didn’t work with Debord’s spectacle in my dissertation on academic Twitter, except insofar as so many of my conversations during that period were with participant and mentor @KateMfD, whose visual identity on the internet during that time was the cover photo FOR Society of the Spectacle (see below). I spent that intensive and relational research period interacting with Kate while primarily visualizing her as that cover image, which…Debord would probably have something to say about. I’ll leave that one for some other keener to unpack.)

@KateMfD, as I will forever see her in my mind
Anyhoo, while I was musing about spectacle thanks to the mangled mob pageantry of the RNC and its blue-collar billionaire, a Debord reference landed smack on my screen much closer to home.
Because last week for us here was also the extraordinary #DigPed PEI, which brought people from all over PEI education and from the US, UK, and other Canadian provinces together for three days of intensive engagement with ideas and tools – Twitter among them. And in one of the (so far very positive and thought-provoking) anonymous feedback forms I solicited afterwards, a participant brought up Debord and spectacle, as related to that individual’s residual hesitancy about social media.
And so I thought, clearly this is a combo endorsement from the universe to go back & read me some Debord.
(After all, beyond politics and societal participation, how many of my household’s personal and professional relationships find communicative and affective expression in Facebook/Twitter/Instagram? What about the casual but relationship-augmenting encounters that Pokemon Go has created for my kids and, erm, me this past week?)
***
So I did. Spoiler? I don’t, ontologically, buy the ways Debord separates society and the subject, and the implied essentialism of a reality outside the spectacle…which is why there was no Debord in my thesis. Still, there’s something to his idea of the spectacle I think we all ought to be digging into and trying to grapple with, especially those of us who see ourselves as educators. Or, um, people who don’t want the world to burn. Or both.
It’s this. What I took out of seventy cobbled-together minutes of my life spent re-aquainting myself with Debord is:
…the spectacle of contemporary society is about power. Full stop.
(Okay there’s more about identity & commodity & reification but Ima hafta dig into that another day. Or you can. Ping me if you do!)
Debord, on power:
“At the root of the spectacle lies that oldest of all social divisions of labor, the specialization of power. The specialized role played by the spectacle is that of spokesman for all other activities, a sort of diplomatic representative of hierarchical society at its own court, and the source of the only discourse which that society allows itself to hear. Thus the most modern aspect of the spectacle is also at bottom its most archaic” (Debord, p. 8).
In other words, the bread and circuses we are being fed are pretty much naked, craven power subsuming all other forms of societal organization.
So Trump’s bizarre content-free campaign video, above? Just power as spectacle, image circulation subsuming any other form of discourse.
Those English people who voted for Brexit but now don’t want to leave? Who voted as they did as a way of signalling “burn it all down”? A sheer exercise in power, both from the political engineers and from many of the individual voters.
And everything Milo Yiannopoulos ever wrote on Twitter? Same. As Laurie Penny says in what is pretty much a mic drop to this particular cultural moment: “It’s all an act. A choreographed performance by a career sociopath who will claim any cause to further his legend.”
The problem, of course, is what Penny points out: there’s no room in this kind of game for truly believing in much of anything. That’s why the disconnects are so vast and nobody seems to care. The “attention hustlers,” as she calls them, “channel their own narcissism to give voice to the wordless, formless rage of the people neoliberalism left behind.”
Spectacle. Power. The fomenting of archaic hatreds, not because one necessarily believes them…but because they’re there. Because they allow social relationships to be mediated so effectively by images and symbols.
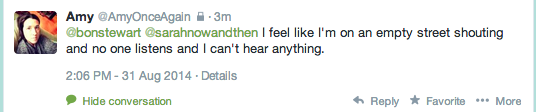
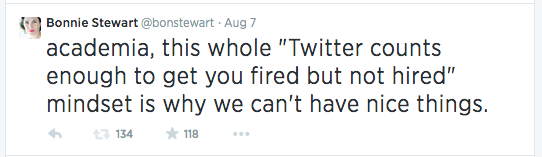
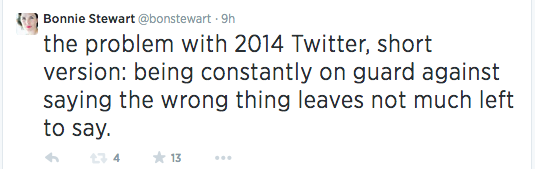
Oh goody. So THAT’s why most of my Twitter feed is so damn bewildered and depressed these days. For those of us who still believe in just about anything beyond the spectacle of power for its own sake, the way the Overton window on this kind of politics and personal practice has shifted is kinda staggering.
Now, given that Debord was writing in 1967 and Ann Coulter’s “career” – to name but one of Penny’s “attention hustlers” – pre-dates social media by at least a decade, Twitter itself nor social media more generally obviously can’t be the source of the spectacle. I don’t actually even believe it’s a more pure or powerful instantiation of the spectacle than television, especially in cable news territory.
But I don’t have cable news on when I work. I don’t spend my professional days with TV constantly in the background.
Whereas Twitter – for me, Twitter even more than Facebook – has been, for the past six or seven years, a constant presence. It’s a stream I dip in and out of as I work, even when it is not the site of my work…and it has been a rich source of connections and conversations and resources FOR that work as well as a space through which my work and voice have been amplified.
But it is also part of the spectacle-ization of broadcast media, part of the crush of the attention economy within which we all swim these days whether we sign up for Pinterest or Twitter or Instagram or no. Because our narratives are all filtered through the spectacle and its steroids of scandal and somewhere after years of 24-hour news cycles and Twitter fights and identity commodification, we all just seem to be rolling down hill in the same unfortunate handbasket, labelled “power.”
Or that’s how it felt this week.
I’m not quite done with Debord, I don’t think. Gonna try again – next week – to figure out what it means to be an educator in the midst of this sea of media and spectacle in which we all swim, and think about the ways in which social media in particular are handmaidens of spectacle…and yet maybe also means of subverting the spectacle that mass media and politics serve up? Maybe.
We’ll see. That’s next week. For the remainder of this week, I’ll just be over in the corner here rocking gently and staring at the wall trying to figure out how to get through another 5+ months of 2016. Join me! I have jellybeans.